Mock server
Mock, match, modify and manipulate a HTTP request/response payload using flexible expectations with types


Navigation
Basics
Install
npm i @n1k1t/mock-serverHow it works
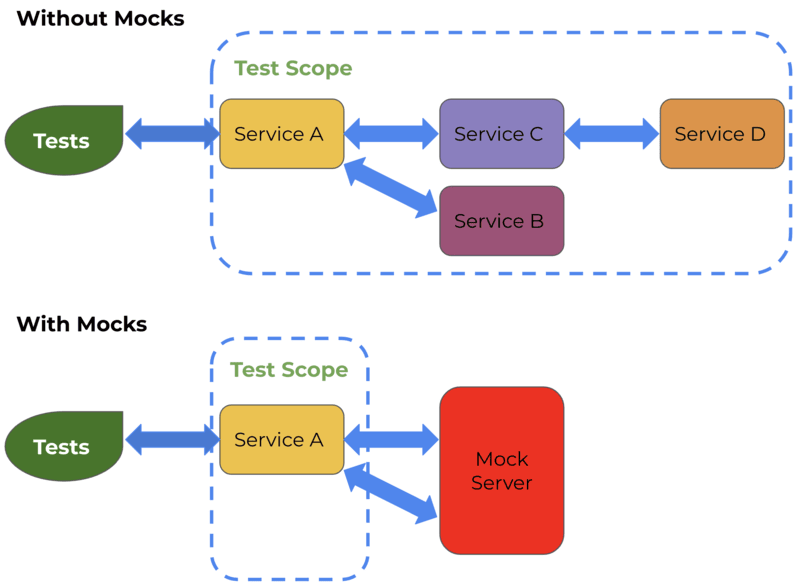
According on the picture above, main idea is to generate or modify response from some backend service. The mock server provides many scenarios to do that
In case of mocking without request forwarding:
- Start mock server (for example on
localhost:8080) - Register expectation using CLI (cURL) or application lib
- Make request to
localhost:8080/...- The mock server matches a request payload with registered expectations
- Build a response using an expectation configuration
In case of mocking with request forwarding:
- Lets imagine that you have a service that hosts on
localhost:8081 - Start mock server (for example on
localhost:8080) - Register expectation using CLI (cURL) or application lib
- Make request to
localhost:8080/...- The mock server matches a request payload with registered expectations
- Next is forwarding a request payload to
localhost:8081/... - Using response fetched from
localhost:8081/...the mock server builds a response
Start
CLI
npx mock -h localhost -p 8080JavaScript
const { MockServer } = require('@n1k1t/mock-server');
MockServer.start({ host: 'localhost', port: 8080 });TypeScript
import { MockServer } from '@n1k1t/mock-server';
MockServer.start({ host: 'localhost', port: 8080 });GUI
The mock server provides built-in web panel to track everything that is going through. There are two tabs Expectations and History
By default it can be found on /_system/gui of a host of mock server. Example: localhost:8080/_system/gui
Also it provides convenient util to navigate through payload of expectations and requests payload
Mock
Simple examples can be found in expectation creation API
Expectations
Schema
An expectation schema can contain some rules to handle request, response and forward
| Property | Nested | Type | Optional | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| request | Operators | object |
* | Describes a way to catch by request and how to manipulate it |
| response | Operators | object |
* | Describes how to manipulate response. Also can be used to catch response in case of forwarding |
| forward | Forwarding | object |
* | Describes configuration to forward a request to another host |
Example
await server.client.createExpectation({
schema: {
request: {
$and: [],
},
response: {
$or: [],
},
forward: {
baseUrl: 'https://example.com',
url: '/some/path',
},
},
});Forwarding
| Property | Nested | Type | Optional | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| url | | string |
* | Absolute URL to target | |
| baseUrl | | string |
* | Base URL to target. The path will be provided from request | |
| options | | string |
* | Forwarding options | |
| | host | origin |
* | Provides Host header as same as mock server host (if not specified). If specified to origin then value for Host header will be taken from url |
|
| cache | | object |
* | Cache configuration for a payload of forwarded requests | |
| | storage | redis |
* | Storage to read/write a cache | |
| | key | string |
* | Key to get read/write access of cached payload | |
| | prefix | string |
* | Prefix of the key of cache |
|
| | ttl | number |
* | Time to live of cache in seconds |
Context
| Property | Nested | $location |
Type | Optional | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| storage | Storage | | object |
| A storage of container entities |
||
| container | Container | container |
object |
* | A temporary cell in storage. Should be useful to sync expectations between each other or store and use any data each request |
| state | | state |
object |
| An object with custom data | ||
| seed | | seed |
string |
* | Incoming request seed | |
| cache | | cache |
object |
| Cache configuration | ||
| | isEnabled | | boolean |
| Toggle of cache usage | |||
| | key | | string ∣ object |
* | Key to get read/write access of cached payload. Value provided as object will hashed using FNV1A-64 algorithm |
||
| | prefix | | string |
* | Prefix of the key of cache |
||
| | ttl | | number |
* | Time to live of cache in seconds | ||
| incoming | | | object |
| Payload with data of incoming request | ||
| | path | path |
string |
| Incoming request path | ||
| | method | method |
string |
| Incoming request method in uppercase | ||
| | headers | incoming.headers |
object |
| Incoming request headers with keys in lowercase | ||
| | dataRaw | incoming.dataRaw |
string |
| Incoming request source data | ||
| | data | incoming.data |
object |
* | Incoming request parsed data | |
| | query | incoming.query |
object |
* | Incoming request query search parameters | |
| | delay | delay |
number |
* | Delay that can be applied with operators | |
| | error | error |
string |
* | Error that can be applied with operators | |
| outgoing | | | object |
| Payload with data of response | ||
| | status | outgoing.status |
number |
| Response status code | ||
| | headers | outgoing.headers |
number |
| Response headers | ||
| | dataRaw | outgoing.dataRaw |
string |
| Response source data | ||
| | data | outgoing.data |
any |
* | Response data |
Utils
Additional utils in $exec operator
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
context |
A request context |
logger |
Logger of mock server |
mode |
A mode of expectation execution. Has match on catching request or manipulate on manipulation over context |
meta |
A meta of a request |
_ |
Lodash |
d |
DayJS |
faker |
Faker. Uses seed if it was provided |
Operators
!NOTE Each schema that using operators can have only one nested operator. To use more than one operator use
$andor$oroperators
| Operator | Optional | Description |
|---|---|---|
| $has | * | Catches a request/response or checks a payload in context |
| $set | * | Sets payload in context |
| $merge | * | Merges object payload in context with provided $value |
| $remove | * | Removes payload in context |
| $exec | * | Function to catch a request/response or check/manipulate payload in context |
| $and | * | Logical and |
| $or | * | Logical or |
| $not | * | Logical not |
| $if | * | Logical if |
| $switch | * | Logical switch/case |
Example
await server.client.createExpectation({
schema: {
request: {
$and: [
{
$has: {
$location: 'path',
$value: '/foo',
},
},
{
$has: {
$location: 'method',
$value: 'GET',
},
},
],
},
},
});$has
!NOTE
$execoperators have restrictions when it defined overHTTP APIorRemoteClient
| Property | Type (application) | Type (cURL) | Optional | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| $location | string enum |
string enum |
| Location that describes what context entity is selecting for operator to work with | |
| $path | string |
string |
* | Specifies a path to payload using lodash get |
| $jsonPath | string |
string |
* | Specifies a path to payload using JSON path |
| $value | any |
any |
* | Checks by value equality in context using $location (and $path, $jsonPath if it was specified) |
| $valueAnyOf | any[] |
any[] |
* | Checks by any of value equality in context using $location (and $path, $jsonPath if it was specified) |
| $regExp | RegExp |
{ source: string, flags?: string } |
* | Checks by regular expression in context using $location (and $path, $jsonPath if it was specified) |
| $regExpAnyOf | RegExp[] |
{ source: string, flags?: string }[] |
* | Checks by any of regular expression in context using $location (and $path, $jsonPath if it was specified) |
| $match | string ∣ object |
string ∣ object |
* | Checks by minimatch for string and number (example /foo/*/bar or 2**) or similar object by passing object payload in context using $location (and $path, $jsonPath if it was specified) |
| $matchAnyOf | (string ∣ object)[] |
(string ∣ object)[] |
* | Checks by any of minimatch for string and number (example /foo/*/bar or 2**) or similar object by passing object payload in context using $location (and $path, $jsonPath if it was specified) |
| $exec | (payload, utils) => boolean |
string |
* | Checks payload in context by function with arguments where payload is selected entity using $location (and $path, $jsonPath if it was specified) and utils is utils |
Example using application
await server.client.createExpectation({
schema: {
request: {
$has: {
$location: 'path',
$regExp: /^\/foo/,
},
},
},
});Example using cURL
curl -H "Content-type: application/json" -X POST --location "localhost:8080/_system/expectations" --data-binary @- << EOF
{
"schema": {
"request": {
"\$has": {
"\$location": "method",
"\$regExp": { "source": "^\/foo" }
}
}
}
}
EOF$set
!NOTE
$execoperators have restrictions when it defined overHTTP APIorRemoteClient
| Property | Type (application) | Type (cURL) | Optional | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| $location | string enum |
string enum |
| Location that describes what context entity is selecting for operator to work with | |
| $path | string |
string |
* | Specifies a path to payload using lodash get |
| $jsonPath | string |
string |
* | Specifies a path to payload using JSON path |
| $value | any |
any |
* | Sets value to context using $location (and $path, $jsonPath if it was specified) |
| $exec | (payload, utils) => any |
string |
* | Sets payload in context by function with arguments where payload is selected entity using $location (and $path, $jsonPath if it was specified) and utils is utils |
Example using application
await server.client.createExpectation({
schema: {
request: {
$set: {
$location: 'incoming.data',
$path: 'foo',
$exec: (payload, { _ }) => _.clamp(payload, 0, 10),
},
},
},
});Example using cURL
curl -H "Content-type: application/json" -X POST --location "localhost:8080/_system/expectations" --data-binary @- << EOF
{
"schema": {
"request": {
"\$set": {
"\$location": "incoming.data",
"\$path": "foo",
"\$exec": "_.clamp(payload, 0, 10)"
}
}
}
}
EOF$merge
!NOTE
$execoperators have restrictions when it defined overHTTP APIorRemoteClient
| Property | Type (application) | Type (cURL) | Optional | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| $location | string enum |
string enum |
| Location that describes what context entity is selecting for operator to work with | |
| $path | string |
string |
* | Specifies a path to payload using lodash get |
| $jsonPath | string |
string |
* | Specifies a path to payload using JSON path |
| $value | object |
object |
* | Merges value in context using $location (and $path, $jsonPath if it was specified) |
| $exec | (payload, utils) => any |
string |
* | Merges payload in context by function with arguments where payload is selected entity using $location (and $path, $jsonPath if it was specified) and utils is utils |
Example using application
await server.client.createExpectation({
schema: {
request: {
$merge: {
$location: 'incoming.data',
$value: { has_mocked: true },
},
},
},
});Example using cURL
curl -H "Content-type: application/json" -X POST --location "localhost:8080/_system/expectations" --data-binary @- << EOF
{
"schema": {
"request": {
"\$merge": {
"\$location": "incoming.data",
"\$value": {"has_mocked": true}
}
}
}
}
EOF$remove
| Property | Type (application) | Type (cURL) | Optional | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| $location | string enum |
string enum |
| Location that describes what context entity is selecting for operator to work with | |
| $path | string |
string |
* | Specifies a path to payload using lodash get |
| $jsonPath | string |
string |
* | Specifies a path to payload using JSON path |
Example using application
await server.client.createExpectation({
schema: {
request: {
$remove: { $location: 'outgoing.data' },
},
},
});Example using cURL
curl -H "Content-type: application/json" -X POST --location "localhost:8080/_system/expectations" --data-binary @- << EOF
{
"schema": {
"request": {
"\$remove": {"\$location": "outgoing.data"}
}
}
}
EOF$exec
!NOTE
$execoperators have restrictions when it defined overHTTP APIorRemoteClient
| Type (application) | Type (cURL) | Description |
|---|---|---|
(utils) => boolean ∣ unknown |
string |
Does something you want or catch request/response payload in context by function with arguments where utils is utils |
Example using application
await server.client.createExpectation({
schema: {
request: {
$exec: ({ context, logger }) => {
logger.info(context);
return context.incoming.path === '/foo';
},
},
},
});Example using cURL
curl -H "Content-type: application/json" -X POST --location "localhost:8080/_system/expectations" --data-binary @- << EOF
{
"schema": {
"request": {
"\$exec": "{ logger.info(context); return context.incoming.path === '/foo' }"
}
}
}
EOF$and
| Type (application) | Type (cURL) | Description |
|---|---|---|
object[] |
object[] |
Provides operators schemas |
Example using application
await server.client.createExpectation({
schema: {
request: {
$and: [
{ $has: { $location: 'path', $match: 'foo/*' } },
{ $has: { $location: 'method', $valueAnyOf: ['GET', 'POST'] } },
],
},
},
});Example using cURL
curl -H "Content-type: application/json" -X POST --location "localhost:8080/_system/expectations" --data-binary @- << EOF
{
"schema": {
"request": {
"\$and": [
{"\$has": {"\$location": "path", "\$match": "foo/*"}},
{"\$has": {"\$location": "method", "\$valueAnyOf": ["GET", "POST"]}}
]
}
}
}
EOF$or
| Type (application) | Type (cURL) | Description |
|---|---|---|
object[] |
object[] |
Provides operators schemas |
Example using application
await server.client.createExpectation({
schema: {
request: {
$or: [
{ $has: { $location: 'path', $match: 'foo/*' } },
{ $has: { $location: 'method', $valueAnyOf: ['GET', 'POST'] } },
],
},
},
});Example using cURL
curl -H "Content-type: application/json" -X POST --location "localhost:8080/_system/expectations" --data-binary @- << EOF
{
"schema": {
"request": {
"\$or": [
{"\$has": {"\$location": "path", "\$match": "foo/*"}},
{"\$has": {"\$location": "method", "\$valueAnyOf": ["GET", "POST"]}}
]
}
}
}
EOF$not
| Type (application) | Type (cURL) | Description |
|---|---|---|
object |
object |
Provides an operators schema |
Example using application
await server.client.createExpectation({
schema: {
request: {
$not: { $has: { $location: 'path', $match: 'foo/*' } },
},
},
});Example using cURL
curl -H "Content-type: application/json" -X POST --location "localhost:8080/_system/expectations" --data-binary @- << EOF
{
"schema": {
"request": {
"\$not": {"\$has": {"\$location": "path", "\$match": "foo/*"}}
}
}
}
EOF$if
| Property | Type (application) | Type (cURL) | Optional | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| $condition | object |
object |
| Condition to check. Should contain one of $and, $exec, $has, $or or $not operators schema |
|
| $then | object |
object |
* | Logical then. Should contain an operators schema |
| $else | object |
object |
* | Logical else. Should contain an operators schema |
Example using application
await server.client.createExpectation({
schema: {
request: {
$if: {
$condition: { $has: { $location: 'path', $match: 'foo/*' } },
$then: { $set: { $location: 'delay', $value: 5000 } },
$else: { $set: { $location: 'error', $value: 'ECONNABORTED' } },
},
},
},
});Example using cURL
curl -H "Content-type: application/json" -X POST --location "localhost:8080/_system/expectations" --data-binary @- << EOF
{
"schema": {
"request": {
"\$if": {
"\$condition": {"\$has": {"\$location": "path", "\$match": "foo/*"}},
"\$then": {"\$set": {"\$location": "delay", "\$value": 5000}},
"\$else": {"\$set": {"\$location": "error", "\$value": "ECONNABORTED"}}
}
}
}
}
EOF$switch
!NOTE
$execoperators have restrictions when it defined overHTTP APIorRemoteClient
| Property | Type (application) | Type (cURL) | Optional | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| $location | string enum |
string enum |
| Location that describes what context entity is selecting for operator to work with | |
| $cases | Record<string ∣ number, object> |
Record<string ∣ number, object> |
| An object where key is an extracted value from enum using $location (and $path, $exec if it was specified) and value is an operators schema |
|
| $default | object |
object |
* | Default behavior as an operators schema |
| $path | string |
string |
* | Specifies a path to payload using lodash get |
| $exec | (payload, utils) => any |
string |
* | Sets payload in context by function with arguments where payload is selected entity using $location and utils is utils |
Example using application
await server.client.createExpectation({
schema: {
request: {
$switch: {
$location: 'method',
$cases: {
'GET': { $set: { $location: 'delay', $value: 2000 } },
'POST': { $set: { $location: 'delay', $value: 5000 } },
},
$default: {
$set: { $location: 'error', $value: 'ECONNABORTED' }
},
},
},
},
});Example using cURL
curl -H "Content-type: application/json" -X POST --location "localhost:8080/_system/expectations" --data-binary @- << EOF
{
"schema": {
"request": {
"\$switch": {
"\$location": "method",
"\$cases": {
"GET": {"\$set": {"\$location": "delay", "\$value": 2000}},
"POST": {"\$set": {"\$location": "delay", "\$value": 5000}}
},
"\$default": {
"\$set": {"\$location": "error", "\$value": "ECONNABORTED"}
}
}
}
}
}
EOFTypings
The application client lib provides approach to keep typings using function predicate to create or update expectation with a generic argument. The generic type should have the same schema like context
The function predicate provides an object argument with $ that contains simplified API to build typed expectation schemas. Some operators have using predicate that can contain $path, $jsonPath or $exec selectors
Examples
await client.createExpectation<{
incoming: {
query: {
foo: 'a' | 'b' | 'c';
bar?: string;
};
};
}>(({ $ }) => ({
schema: {
request: $.or([
$.has('incoming.query', '$path', 'foo', { $value: 'a' }),
$.has('incoming.query', { $match: { foo: 'b' } }),
]),
},
}));await client.createExpectation<{
incoming: {
query: {
foo: 'a' | 'b' | 'c';
bar?: string;
};
};
outgoing: {
data: {
foo: 'a' | 'b' | 'c';
bar?: {
baz: 'a' | 'b' | 'c';
};
};
};
}>(({ $ }) => ({
schema: {
response: $.and([
$.switch('incoming.query', '$exec', (payload) => payload.foo, {
$cases: {
'a': $.set('outgoing.data', '$path', 'bar.baz', { $value: 'a' }),
'b': $.set('outgoing.data', '$path', 'bar.baz', { $value: 'b' }),
},
}),
$.switch('incoming.query', '$path', 'bar', {
$cases: {
'something': $.set('outgoing.data', '$path', 'bar.baz', { $value: 'c' }),
},
}),
]),
},
}));Storage
Storage is a temporary storage that provides an access to read/write containers
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| find | (key: string ∣ object) => Container ∣ null |
Finds a container in storage. Every key provided as object will hashed using FNV1A-64 algorithm |
| delete | (key: string ∣ object) => Container ∣ null |
Deletes a container in storage. Every key provided as object will hashed using FNV1A-64 algorithm |
| register | (configuration: Container) => Container |
Registers a container in storage (overrides if existent) |
| provide | (configuration: Container) => Container |
Finds or registers a container in storage |
As a temporary storage it has a job to garbage an expired containers. Use containers.expiredCleaningInterval to setup an interval of clearance in configuration
!NOTE See example of usage in containers section below
Containers
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| key | string |
A key of container |
| prefix | string |
A prefix of container |
| payload | object |
An object with custom data |
| ttl | number |
Time to live of container in seconds (default: 1h) |
| expiresAt | number |
An expiration date/time as unix timestamp with milliseconds |
| bind | (key: string ∣ object) => Container |
Binds a container to one more key. Every key provided as object will hashed using FNV1A-64 algorithm |
| unbind | (key: string ∣ object) => Container |
Unbinds a container from key. Every key provided as object will hashed using FNV1A-64 algorithm |
| assign | (payload: object ∣ (payload: object) => object) => Container |
Uses as payload predicate to assign payload values to existent |
| merge | (payload: object ∣ (payload: object) => object) => Container |
Uses as payload predicate to deep merge of payload values with existent |
Example
await client.createExpectation<{
container: {
counter: number;
};
}>(({ $ }) => ({
schema: {
request: $.set('container', {
$exec: (container, { context }) => context.storage
.provide({ key: 'foo', payload: { counter: 0 } })
.assign((payload) => ({ counter: payload.counter + 1 }))
}),
response: $.set('outgoing.data', {
$exec: (payload, { context }) => ({
count: context.container!.payload.counter,
}),
}),
},
}));Cache
!NOTE Cache is usable only to store a payload of forwarded requests
To work with cache the mock server uses ioredis package
To configure it use database.redis configuration on the mock server start options
Example
const server = await MockServer.start({
host: 'localhost',
port: 8080,
databases: {
redis: {
host: 'localhost',
port: 6379,
},
},
});How it works in steps?
- Expectation schema should have
forwardconfiguration specified - Preparing incoming request...
- Preparing request schema in expectation...
- Setting up cache configuration from context or forward.cache...
- If
cache.isEnabledis equalstruethe mock server checks a cache using provided configuration - If
keywas not provided a key for cache will calculated withpath,method,dataandqueryproperty values using FNV1A-64 algorithm - If cache was found then step
7is skipping - Forwarding a request....
- Preparing response schema in expectation...
- Setting up cache configuration from context...
- If
cache.isEnabledis equalstruethe mock server will write a cache over providedttl - Replying...
Example
await client.createExpectation(({ $ }) => ({
schema: {
response: $.set('cache', '$path', 'isEnabled', {
$exec: (payload, { context }) => context.outgoing.status < 400,
}),
forward: {
baseUrl: 'https://example.com',
cache: {
ttl: 30 * 24 * 60 * 60,
},
},
},
}));State
State is a unique storage of each request. It can be used to handle complex expectations
By default an object of state extracts from X-Use-Mock-State in incoming.headers (as serialized json in base64 encoding) or creates an empty object
Example
await client.createExpectation<{
state: {
id?: number;
};
incoming: {
query: {
foo: 'a' | 'b' | 'c';
};
};
outgoing: {
data: {
id: number;
};
};
}>(({ $ }) => ({
schema: {
request: $.and([
$.switch('incoming.query', '$exec', (payload) => payload.foo, {
$cases: {
'a': $.set('state', '$path', 'id', { $value: 1 }),
'b': $.set('state', '$path', 'id', { $value: 2 }),
},
}),
]),
response: $.set('outgoing.data', {
$exec: (payload, { state }) => ({ id: state.id ?? 0 }),
}),
},
}));Seeds
Seeds can help to generate content with the same values each request using faker
By default a number of seed takes from X-Use-Mock-Seed in incoming.headers
Example
await client.createExpectation(({ $ }) => ({
schema: {
request: $.and([
$.set('seed', { $exec: (seed) => seed ?? 123 }),
]),
response: $.set('outgoing.data', {
$exec: (payload, { faker }) => ({
id: faker.number.int({ max: 1000, min: 500 }),
first_name: faker.person.firstName('male'),
last_name: faker.person.lastName('male'),
}),
}),
},
}));XML
The mock server uses the fast-xml-parser package to parse and serialize XML payload with options:
{
ignoreAttributes: false,
}To define a incoming.data as XML in incoming request incoming.headers should have Content-Type: application/xml.
The same with outgoing.data and outgoing.headers
Example of serialized XML
<tag type="default">
<nested type="nested">456</nested>
123
</tag>Example of parsed XML
{
"tag":{
"nested":{
"#text":456,
"@_type":"nested"
},
"#text":123,
"@_type":"default"
}
}To parse an XML manually the application lib provides utils:
import { parsePayload, serializePayload } from '@n1k1t/mock-server';
const parsed = parsePayload('xml', '<tag>123</tag>'); // { tag: 123 }
const serialized = serializePayload('xml', parsed); // '<tag>123</tag>'API
The mock server provides 3 different ways to work with. There are: HTTP API (eg using cURL), RemoteClient provided by application lib to connect and work with existent mock server on another host and MockServer.client on the same host (application script)
The HTTP API and RemoteClient have some usage restrictions like:
- Every
$execoperator cannot have an access to variables outside the function. If you need to use some extra variables or modules that implemented in outer scope you have to use theMockServer.clientto setup everything on the mock server side host - Plugins are not supported
Ping
INPUT → GET /_system/ping
OUTPUT
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
string |
A pong message |
Using cURL
curl -H "Content-type: application/json" --location "localhost:8080/_system/ping"Using application lib on server side
import { MockServer } from '@n1k1t/mock-server';
const server = await MockServer.start({ host: 'localhost', port: 8080 });
await server.client.ping();Using application lib on remotely
import { RemoteClient } from '@n1k1t/mock-server';
const client = await RemoteClient.connect({ host: 'localhost', port: 8080 });
await client.ping();Create expectation
INPUT → POST /_system/expectations
| Property | Nested | Type | Optional | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| schema | Schema | object |
| An expectation schema | |
| name | | string |
* | A preferred name for an expectation |
OUTPUT
| Property | Nested | Type | Optional | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | | string |
| An expectation ID | ||
| name | | string |
| An expectation name | ||
| schema | Schema | object |
| Provided schema |
Using cURL
curl -H "Content-type: application/json" -X POST --location "localhost:8080/_system/expectations" --data-binary @- << EOF
{
"schema": {
"request": {
"\$has": {
"\$location": "method",
"\$value": "GET"
}
}
}
}
EOFUsing application lib on server side
import { MockServer } from '@n1k1t/mock-server';
const server = await MockServer.start({ host: 'localhost', port: 8080 });
const expectation = await server.client.createExpectation({
schema: {
request: {
$has: {
$location: 'method',
$value: 'GET',
},
},
},
});
console.log('Mock expectation has created', expectation.id);Using application lib on remotely
import { RemoteClient } from '@n1k1t/mock-server';
const client = await RemoteClient.connect({ host: 'localhost', port: 8080 });
const expectation = await client.createExpectation({
schema: {
request: {
$has: {
$location: 'method',
$value: 'GET',
},
},
},
});
console.log('Mock expectation has created', expectation.id);Update expectation
INPUT → PUT /_system/expectations
| Property | Nested | Type | Optional | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | | string |
| ID of a registered expectation | ||
| set | | object |
| A payload to set | ||
| | name | string |
* | A preferred name for an expectation | |
| | schema | Schema | * | An expectation schema |
OUTPUT
| Property | Nested | Type | Optional | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | | string |
| An expectation ID | ||
| name | | string |
| An expectation name | ||
| schema | Schema | object |
| Provided schema |
Using cURL
curl -H "Content-type: application/json" -X PUT --location "localhost:8080/_system/expectations" --data-binary @- << EOF
{
"id": "...",
"set": {"name": "The expectation"}
}
EOFUsing application lib on server side
import { MockServer } from '@n1k1t/mock-server';
const server = await MockServer.start({ host: 'localhost', port: 8080 });
const expectation = await server.client.updateExpectation({
id: '...',
set: { name: 'The expectation' }
});
console.log('Mock expectation has updated', expectation);Using application lib on remotely
import { RemoteClient } from '@n1k1t/mock-server';
const client = await RemoteClient.connect({ host: 'localhost', port: 8080 });
const expectation = await client.updateExpectation({
id: '...',
set: { name: 'The expectation' }
});
console.log('Mock expectation has updated', expectation);Delete expectation
INPUT → DELETE /_system/expectations
| Property | Nested | Type | Optional | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ids | | string[] |
* | An expectation IDs list to delete. Or delete all expectations if not provided |
Using cURL
curl -H "Content-type: application/json" -X DELETE --location "localhost:8080/_system/expectations" --data-binary @- << EOF
{
"ids": ["..."]
}
EOFUsing application lib on server side
import { MockServer } from '@n1k1t/mock-server';
const server = await MockServer.start({ host: 'localhost', port: 8080 });
await server.client.deleteExpectations({
ids: ['...'],
});Using application lib on remotely
import { RemoteClient } from '@n1k1t/mock-server';
const client = await RemoteClient.connect({ host: 'localhost', port: 8080 });
await client.deleteExpectations({
ids: ['...'],
});Additional
Configuration
!NOTE Configuration must be provided in the same script like mock server
import { config } from '@n1k1t/mock-server';
config.merge({
logger: {
level: 'D', // Logger level (default: D)
},
history: {
limit: 100, // Limit for history of requests (default: 100)
},
containers: {
expiredCleaningInterval: 60 * 60, // Expired containers cleaning interval in seconds (default: 1h)
},
});Logger
!NOTE Configuration must be provided in the same script like mock server
import { Logger } from '@n1k1t/mock-server';
// It defines your own logger methods
Logger.useExternal({
debug: (...messages: string[]) => console.debug(...messages),
info: (...messages: string[]) => console.log(...messages),
warn: (...messages: string[]) => console.warn(...messages),
error: (...messages: string[]) => console.error(...messages),
fatal: (...messages: string[]) => console.error(...messages),
});
// It defines a JSON serializers to mask some private data by keys on objects
Logger.useSerializers({
cvv: () => '***',
card: (payload: string) => payload.slice(0, 8) + 'xxxx',
});Meta
Some loggers (like banyan and etc) provide a meta context for logs with some data. To keep a meta contexts between requests the mock server provides a metaStorage using native node AsyncLocalStorage.
The metaStorage.provide() returns an instance of meta that contains basic data like:
| Property | Type | Optional | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| operationId | string |
| UUID v4 | |
| requestId | string |
* | X-Request-Id from incoming.headers |
Setup
import { Logger, metaStorage } from '@n1k1t/mock-server';
// Some external logger with meta context support
const external = {...};
// It defines your own logger methods
Logger.useExternal({
debug: (...messages: string[]) => external.debug(metaStorage.provide(), ...messages),
info: (...messages: string[]) => external.log(metaStorage.provide(), ...messages),
warn: (...messages: string[]) => external.warn(metaStorage.provide(), ...messages),
error: (...messages: string[]) => external.error(metaStorage.provide(), ...messages),
fatal: (...messages: string[]) => external.error(metaStorage.provide(), ...messages),
});Usage
await server.client.createExpectation({
schema: {
request: {
$exec: ({ context, logger }) => {
// Here logger should have a meta context like { operationId: '...' }
logger.info('Before')
},
$exec: ({ context, logger, meta }) => {
// It enriches meta context for further logs of request
meta.merge({ foo: 'bar' });
},
$exec: ({ context, logger, meta }) => {
// Now logger should have a meta context like { foo: 'bar', operationId: '...' }
logger.info('After')
},
},
},
});%20div%201000&label=coverage)