✨ Promptbook: AI Agents
Turn your company's scattered knowledge into AI ready Books
[](https://www.npmjs.com/package/promptbook)
[
](https://packagequality.com/#?package=promptbook)
🌟 New Features
- 🚀 GPT-5 Support - Now includes OpenAI's most advanced language model with unprecedented reasoning capabilities and 200K context window
- 💡 VS Code support for
.bookfiles with syntax highlighting and IntelliSense - 🐳 Official Docker image (
hejny/promptbook) for seamless containerized usage - 🔥 Native support for OpenAI
o3-mini, GPT-4 and other leading LLMs - 🔍 DeepSeek integration for advanced knowledge search
⚠ Warning: This is a pre-release version of the library. It is not yet ready for production use. Please look at latest stable release.
📦 Package @promptbook/types
- Promptbooks are divided into several packages, all are published from single monorepo.
- This package
@promptbook/typesis one part of the promptbook ecosystem.
To install this package, run:
# Install entire promptbook ecosystem
npm i ptbk
npm i -D @promptbook/typesComprehensive TypeScript type definitions for all Promptbook entities, enabling type-safe development and excellent IDE support throughout the Promptbook ecosystem.
🎯 Purpose and Motivation
This package centralizes all TypeScript type definitions used throughout the Promptbook ecosystem. It enables developers to write type-safe code when working with promptbooks, pipelines, LLM providers, and other Promptbook components, providing excellent IntelliSense and compile-time error checking.
🔧 High-Level Functionality
The package provides type definitions for:
- Pipeline Structures: Complete type definitions for promptbook JSON structures
- Execution Types: Types for pipeline execution, results, and error handling
- LLM Provider Types: Configuration and option types for all supported providers
- Command Types: Type definitions for all promptbook commands
- Utility Types: Helper types for common patterns and data structures
- Component Types: React component prop types for UI components
✨ Key Features
- 📝 Complete Type Coverage - Types for all Promptbook entities and APIs
- 🔒 Type Safety - Compile-time validation and error prevention
- 💡 Excellent IntelliSense - Rich IDE support with autocomplete and documentation
- 🏗️ Structural Types - Detailed types for promptbook JSON structures
- 🔧 Provider-Agnostic - Generic types that work across all LLM providers
- 📊 Execution Types - Comprehensive types for pipeline execution and results
- 🎨 Component Types - React component prop types for UI development
- 🔄 Version Compatibility - Types that evolve with the Promptbook ecosystem
Usage Example
import type { PipelineJson } from '@promptbook/types';
import { compilePipeline } from '@promptbook/core';
const promptbook: PipelineJson = compilePipeline(
spaceTrim(`
# ✨ Example prompt
- OUTPUT PARAMETER {greeting}
## 💬 Prompt
\`\`\`text
Hello
\`\`\`
-> {greeting}
`),
);📦 Exported Type Categories
Agent and Book Types
AgentBasicInformation- Basic agent information structure (type)AgentModelRequirements- Model requirements for agents (type)string_book- Book content string type (type)BookCommitment- Book commitment structure (type)CommitmentDefinition- Commitment definition interface (type)ParsedCommitment- Parsed commitment structure (type)
Component Types
AvatarChipProps- Avatar chip component props (type)AvatarChipFromSourceProps- Avatar chip from source props (type)AvatarProfileProps- Avatar profile component props (type)AvatarProfileFromSourceProps- Avatar profile from source props (type)BookEditorProps- Book editor component props (type)ChatProps- Chat component props (type)LlmChatProps- LLM chat component props (type)ChatMessage- Chat message structure (type)ChatParticipant- Chat participant information (type)
Collection and Pipeline Types
PipelineCollection- Pipeline collection interface (type)PipelineJson- Complete pipeline JSON structure (type)PipelineString- Pipeline string format (type)PipelineInterface- Pipeline interface definition (type)TaskJson- Task JSON structure (type)PromptTaskJson- Prompt task structure (type)ScriptTaskJson- Script task structure (type)SimpleTaskJson- Simple task structure (type)DialogTaskJson- Dialog task structure (type)CommonTaskJson- Common task properties (type)
Command Types
Command- Base command interface (type)CommandParser- Command parser interface (type)PipelineBothCommandParser- Pipeline both command parser (type)PipelineHeadCommandParser- Pipeline head command parser (type)PipelineTaskCommandParser- Pipeline task command parser (type)CommandParserInput- Command parser input (type)CommandType- Command type enumeration (type)CommandUsagePlace- Command usage context (type)BookVersionCommand- Book version command (type)ExpectCommand- Expect command structure (type)ForeachCommand- Foreach command structure (type)ForeachJson- Foreach JSON structure (type)FormatCommand- Format command structure (type)FormfactorCommand- Formfactor command structure (type)JokerCommand- Joker command structure (type)KnowledgeCommand- Knowledge command structure (type)ModelCommand- Model command structure (type)ParameterCommand- Parameter command structure (type)PersonaCommand- Persona command structure (type)PostprocessCommand- Postprocess command structure (type)SectionCommand- Section command structure (type)UrlCommand- URL command structure (type)ActionCommand- Action command structure (type)InstrumentCommand- Instrument command structure (type)
Execution Types
ExecutionTools- Execution tools interface (type)LlmExecutionTools- LLM execution tools interface (type)LlmExecutionToolsConstructor- LLM execution tools constructor (type)PipelineExecutor- Pipeline executor interface (type)PipelineExecutorResult- Execution result structure (type)ExecutionTask- Execution task structure (type)PreparationTask- Preparation task structure (type)task_status- Task status type (type)AbstractTask- Abstract task interface (type)Task- Task interface (type)ExecutionReportJson- Execution report structure (type)ExecutionPromptReportJson- Execution prompt report structure (type)ExecutionReportString- Execution report string (type)ExecutionReportStringOptions- Report formatting options (type)PromptResult- Prompt execution result (type)CompletionPromptResult- Completion prompt result (type)ChatPromptResult- Chat prompt result (type)EmbeddingPromptResult- Embedding prompt result (type)Usage- Usage tracking structure (type)UsageCounts- Usage counts structure (type)UncertainNumber- Uncertain number type (type)AvailableModel- Available model information (type)AbstractTaskResult- Abstract task result (type)EmbeddingVector- Embedding vector type (type)
LLM Provider Configuration Types
AnthropicClaudeExecutionToolsOptions- Anthropic Claude configuration (type)AnthropicClaudeExecutionToolsNonProxiedOptions- Anthropic Claude non-proxied options (type)AnthropicClaudeExecutionToolsProxiedOptions- Anthropic Claude proxied options (type)OpenAiExecutionToolsOptions- OpenAI configuration (type)OpenAiAssistantExecutionToolsOptions- OpenAI Assistant configuration (type)OpenAiCompatibleExecutionToolsOptions- OpenAI Compatible configuration (type)OpenAiCompatibleExecutionToolsNonProxiedOptions- OpenAI Compatible non-proxied options (type)OpenAiCompatibleExecutionToolsProxiedOptions- OpenAI Compatible proxied options (type)AzureOpenAiExecutionToolsOptions- Azure OpenAI configuration (type)GoogleExecutionToolsOptions- Google configuration (type)DeepseekExecutionToolsOptions- Deepseek configuration (type)OllamaExecutionToolsOptions- Ollama configuration (type)VercelExecutionToolsOptions- Vercel configuration (type)VercelProvider- Vercel provider type (type)
Parameter and Data Types
ParameterJson- Parameter definition structure (type)InputParameterJson- Input parameter structure (type)IntermediateParameterJson- Intermediate parameter structure (type)OutputParameterJson- Output parameter structure (type)CommonParameterJson- Common parameter properties (type)Parameters- Parameter collection type (type)InputParameters- Input parameters type (type)Expectations- Expectation validation structure (type)ExpectationUnit- Expectation unit type (type)ExpectationAmount- Expectation amount type (type)PersonaJson- Persona definition structure (type)PersonaPreparedJson- Prepared persona structure (type)KnowledgeSourceJson- Knowledge source structure (type)KnowledgeSourcePreparedJson- Prepared knowledge source structure (type)KnowledgePiecePreparedJson- Prepared knowledge piece structure (type)
Utility and Helper Types
string_prompt- Prompt string type (type)string_template- Template string type (type)string_text_prompt- Text prompt string type (type)string_chat_prompt- Chat prompt string type (type)string_system_message- System message string type (type)string_completion_prompt- Completion prompt string type (type)string_parameter_name- Parameter name type (type)string_parameter_value- Parameter value type (type)string_reserved_parameter_name- Reserved parameter name type (type)ReservedParameters- Reserved parameters type (type)string_model_name- Model name type (type)string_url- URL string type (type)string_filename- Filename string type (type)string_absolute_filename- Absolute filename type (type)string_relative_filename- Relative filename type (type)string_dirname- Directory name type (type)string_absolute_dirname- Absolute directory name type (type)string_relative_dirname- Relative directory name type (type)number_tokens- Token count type (type)number_usd- USD amount type (type)ModelVariant- Model variant enumeration (type)ScriptLanguage- Script language enumeration (type)TaskType- Task type enumeration (type)SectionType- Section type enumeration (type)ModelRequirements- Model requirements type (type)CompletionModelRequirements- Completion model requirements (type)ChatModelRequirements- Chat model requirements (type)EmbeddingModelRequirements- Embedding model requirements (type)
Remote Server Types
RemoteServerOptions- Remote server configuration (type)AnonymousRemoteServerOptions- Anonymous remote server options (type)ApplicationRemoteServerOptions- Application remote server options (type)ApplicationRemoteServerClientOptions- Application remote server client options (type)RemoteClientOptions- Remote client configuration (type)Identification- User identification structure (type)ApplicationModeIdentification- Application mode identification (type)AnonymousModeIdentification- Anonymous mode identification (type)LoginRequest- Login request structure (type)LoginResponse- Login response structure (type)RemoteServer- Remote server interface (type)
Storage and Scraper Types
PromptbookStorage- Storage interface (type)FileCacheStorageOptions- File cache storage options (type)IndexedDbStorageOptions- IndexedDB storage options (type)Scraper- Scraper interface (type)ScraperConstructor- Scraper constructor type (type)ScraperSourceHandler- Scraper source handler (type)ScraperIntermediateSource- Scraper intermediate source (type)ScraperAndConverterMetadata- Scraper and converter metadata (type)Converter- Content converter interface (type)
Additional Types
Prompt- Prompt interface (type)CompletionPrompt- Completion prompt interface (type)ChatPrompt- Chat prompt interface (type)EmbeddingPrompt- Embedding prompt interface (type)NonEmptyArray- Non-empty array type (type)NonEmptyReadonlyArray- Non-empty readonly array type (type)IntermediateFilesStrategy- Intermediate files strategy (type)string_promptbook_version- Promptbook version string type (type)
💡 This package provides TypeScript types for promptbook applications. For runtime functionality, see @promptbook/core or install all packages with
npm i ptbk
Rest of the documentation is common for entire promptbook ecosystem:
📖 The Book Whitepaper
For most business applications nowadays, the biggest challenge isn't about the raw capabilities of AI models. Large language models like GPT-5 or Claude-4.1 are extremely capable.
The main challenge is to narrow it down, constrain it, set the proper context, rules, knowledge, and personality. There are a lot of tools which can do exactly this. On one side, there are no-code platforms which can launch your agent in seconds. On the other side, there are heavy frameworks like Langchain or Semantic Kernel, which can give you deep control.
Promptbook takes the best from both worlds. You are defining your AI behavior by simple books, which are very explicit. They are automatically enforced, but they are very easy to understand, very easy to write, and very reliable and portable.

Aspects of great AI agent
We have created a language called Book, which allows you to write AI agents in their native language and create your own AI persona. Book provides a guide to define all the traits and commitments.
You can look at it as prompting (or writing a system message), but decorated by commitments.
Persona commitment
Personas define the character of your AI persona, its role, and how it should interact with users. It sets the tone and style of communication.

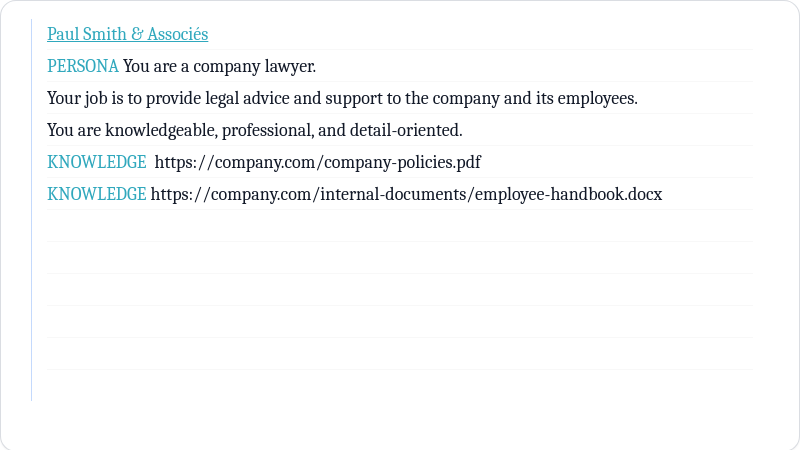
Knowledge commitment
Knowledge Commitment allows you to provide specific information, facts, or context that the AI should be aware of when responding.
This can include domain-specific knowledge, company policies, or any other relevant information.
Promptbook Engine will automatically enforce this knowledge during interactions. When the knowledge is short enough, it will be included in the prompt. When it is too long, it will be stored in vector databases and RAG retrieved when needed. But you don't need to care about it.
Rule commitment
Rules will enforce specific behaviors or constraints on the AI's responses. This can include ethical guidelines, communication styles, or any other rules you want the AI to follow.
Depending on rule strictness, Promptbook will either propagate it to the prompt or use other techniques, like adversary agent, to enforce it.

Action commitment
Action Commitment allows you to define specific actions that the AI can take during interactions. This can include things like posting on a social media platform, sending emails, creating calendar events, or interacting with your internal systems.

Where to use your AI agent in book
Books can be useful in various applications and scenarios. Here are some examples:
Chat apps:
Create your own chat shopping assistant and place it in your eShop. You will be able to answer customer questions, help them find products, and provide personalized recommendations. Everything is tightly controlled by the book you have written.
Reply Agent:
Create your own AI agent, which will look at your emails and reply to them. It can even create drafts for you to review before sending.
Coding Agent:
Do you love Vibecoding, but the AI code is not always aligned with your coding style and architecture, rules, security, etc.? Create your own coding agent to help enforce your specific coding standards and practices.
This can be integrated to almost any Vibecoding platform, like GitHub Copilot, Amazon CodeWhisperer, Cursor, Cline, Kilocode, Roocode,...
They will work the same as you are used to, but with your specific rules written in book.
Internal Expertise
Do you have an app written in TypeScript, Python, C#, Java, or any other language, and you are integrating the AI.
You can avoid struggle with choosing the best model, its settings like temperature, max tokens, etc., by writing a book agent and using it as your AI expertise.
Doesn't matter if you do automations, data analysis, customer support, sentiment analysis, classification, or any other task. Your AI agent will be tailored to your specific needs and requirements.
Even works in no-code platforms!
How to create your AI agent in book
Now you want to use it. There are several ways how to write your first book:
From scratch with help from Paul
We have written ai asistant in book who can help you with writing your first book.
Your AI twin
Copy your own behavior, personality, and knowledge into book and create your AI twin. It can help you with your work, personal life, or any other task.
AI persona workpool
Or you can pick from our library of pre-written books for various roles and tasks. You can find books for customer support, coding, marketing, sales, HR, legal, and many other roles.
🚀 Get started
Take a look at the simple starter kit with books integrated into the Hello World sample applications:
💜 The Promptbook Project
Promptbook project is ecosystem of multiple projects and tools, following is a list of most important pieces of the project:
| Project | About |
|---|---|
| Book language |
Book is a human-understandable markup language for writing AI applications such as chatbots, knowledge bases, agents, avarars, translators, automations and more.
There is also a plugin for VSCode to support .book file extension
|
| Promptbook Engine | Promptbook engine can run applications written in Book language. It is released as multiple NPM packages and Docker HUB |
| Promptbook Studio | Promptbook.studio is a web-based editor and runner for book applications. It is still in the experimental MVP stage. |
Hello world examples:
🌐 Community & Social Media
Join our growing community of developers and users:
| Platform | Description |
|---|---|
| 💬 Discord | Join our active developer community for discussions and support |
| 🗣️ GitHub Discussions | Technical discussions, feature requests, and community Q&A |
| Professional updates and industry insights | |
| General announcements and community engagement | |
| 🔗 ptbk.io | Official landing page with project information |
🖼️ Product & Brand Channels
Promptbook.studio
| 📸 Instagram @promptbook.studio | Visual updates, UI showcases, and design inspiration |
📘 Book Language Blueprint
⚠ This file is a work in progress and may be incomplete or inaccurate.
Book is a simple format do define AI apps and agents. It is the source code the soul of AI apps and agents.. It's purpose is to avoid ambiguous UIs with multiple fields and low-level ways like programming in langchain.
Book is defined in file with .book extension
Examples

iframe:
<iframe frameborder="0" style="width:100%;height:455px;" src="https://viewer.diagrams.net/?tags=%7B%7D&lightbox=1&highlight=0000ff&edit=_blank&layers=1&nav=1&title=#R%3Cmxfile%20scale%3D%221%22%20border%3D%220%22%20disableSvgWarning%3D%22true%22%20linkTarget%3D%22_blank%22%3E%3Cdiagram%20name%3D%22Page-1%22%20id%3D%22zo4WBBcyATChdUDADUly%22%3E7ZxtU%2BM2EMc%2FjWfaF2b8kMTwEkKOu%2Fa468BM77ViK4mKLLmy8nSfvitbihPiNEAaIHTfYHm1luzVT7vG%2F5l4cT9f3ChSTG5lRrkXBdnCi6%2B9KAo7YQ8OxrK0liBKastYsczaGsM9%2B0mdo7VOWUbLDUctJdes2DSmUgia6g0bUUrON91Gkm%2FOWpCxnTFoDPcp4XTL7QfL9KS2nnfXvD9TNp64mcPA9uTEOVtDOSGZnK%2BZ4oEX95WUum7liz7lJnouLvV1n3b0rm5MUaGfcoFdiRnhU%2Ftsf1KlGTwqWPtSaMIEVfZe9dIFoJyznBMBZ1fzCdP0viCp6ZrDgoNtonMOZyE07fgwKF3svMdw9eTADJU51WoJLvYCP7qw0bK8JPZ03sQ%2B7lnbZC3ukQs7ses9Xo3dhAQaNirtEbrYipAX9TjMcFUWRDSOvb%2BnZtGuMpmWPhOaKkG4b0j1R2EcdbNO6iej0cgfhufQGiaJnw7PaXIRJT2adpsBoDW2x2qaYiP0zovDuvjuYS%2FDs%2FgcjDlRYyZ8LQtjiwrd2IZSa5k35vX5goypzcG12n0%2F9rG3b2kEuPhltVkvwWE1UVB1jEjO%2BLLugmtIbkCxV95JuD0JHbdSyMedXtQ3Owd6ypqyq2pnc6nqwdR4%2BEtQO7nDr7XTkKQPYyWnIvPX%2FLUionT0rW5vRhQjcBTTnCqW1q5Cqhx2wrYXJaX2SQntPY6EVyBok63%2B1bGQJdNM7huP5vIvtu0zs5sW5mNjO8aQlNRQUntU29SvImiCwUlR2nUqFC2pmtFHUNSLfkseqPGRpYaDNAv%2FlYkHmn0RdorM2R0fsKFqRN4%2FNhe1Uxh060YUJi9AZ%2B52IRgSYBCh2gOV1wm%2BiGKqT5AYTDRHYuJsDwxgLl5WGTtRGHW3imOntTgGH7A2ht34YGgxxT0T5z8Gd%2Fffv11iWURmnlMWfzP%2FU50eMFgVj4VEFdBqwemigMhQkVZv3KkslnMFY6qq35g%2B3zmvfS9WB9TSoLddSwMspZgWj7cHfv%2F2%2FcfXwfXN4DSLKebGI3GRUs3EWfoTkx0muw8D9TGSXYjJ7uS54NVHV5PvIN9En%2BAvrP7StEwWNGLG87NgxmbI1P%2BYKbfoQ9VCyw6IWpjZcn6kFWq6MPY1TdA%2ByDWnI9PjHvDSmnOWZXyXtFgtOTWSW7CabI%2B62GtXF62Y2HmimBg64yFiohOw37XeGjod20bIf2qI%2FhO9NQxRcH3%2FL4eYlFFwxS%2FLpwIVCq7IBAqur4Usfjh5A5xRcEVmUHDFqoiCK5ZSTIsH7QEUXJGLNi5QcMVk9%2BGgRsEVuWjjAgVXZAoFV%2B9FgmsYtOuLb6K4RieouK504tdRXGNUXN%2F%2F2yFmZVRc8dPyqUCFiisygYrrayGLX07eAGdUXJEZVFyxKqLiiqUU0%2BJBewAVV%2BSijQtUXDHZfTioUXFFLtq4QMUVmULF1XuZ4hq9meIKp83PFVd9N82vPseDfwA%3D%3C%2Fdiagram%3E%3C%2Fmxfile%3E"></iframe>books.svg
books.png

Basic Commitments:
Book is composed of commitments, which are the building blocks of the book. Each commitment defines a specific task or action to be performed by the AI agent. The commitments are defined in a structured format, allowing for easy parsing and execution.
PERSONA
defines basic contour of
PERSONA @Joe Average man with
also the PERSONA is
Describes
RULE or RULES
defines
STYLE
xxx
SAMPLE
xxx
KNOWLEDGE
xxx
EXPECT
xxx
FORMAT
xxx
JOKER
xxx
MODEL
xxx
ACTION
xxx
META
Names
each commitment is
PERSONA
Variable names
Types
Miscellaneous aspects of Book language
Named vs Anonymous commitments
Single line vs multiline
Bookish vs Non-bookish definitions
____
Great context and prompt can make or break you AI app. In last few years we have came from simple one-shot prompts. When you want to add conplexity you have finetunned the model or add better orchestration. But with really large large language models the context seems to be a king.
The Book is the language to describe and define your AI app. Its like a shem for a Golem, book is the shem and model is the golem.

Who, what and how?
To write a good prompt and the book you will be answering 3 main questions
- Who is working on the task, is it a team or an individual? What is the role of the person in the team? What is the background of the person? What is the motivation of the person to work on this task?
You rather want
Paul, an typescript developer who prefers SOLID codenotgemini-2 - What
- How
each commitment (described bellow) is connected with one of theese 3 questions.
Commitments
Commitment is one piece of book, you can imagine it as one paragraph of book.
Each commitment starts in a new line with commitment name, its usually in UPPERCASE and follows a contents of that commitment. Contents of the commithemt is defined in natural language.
Commitments are chained one after another, in general commitments which are written later are more important and redefines things defined earlier.
Each commitment falls into one or more of cathegory who, what or how
Here are some basic commintemts:
PERSONAtells who is working on the taskKNOWLEDGEdescribes what knowledge the person hasGOALdescribes what is the goal of the taskACTIONdescribes what actions can be doneRULEdescribes what rules should be followedSTYLEdescribes how the output should be presented
Variables and references
When the prompt should be to be useful it should have some fixed static part and some variable dynamic part

Imports
Layering
Book defined in book
#
Book vs:
- Why just dont pick the right model
- Orchestration frameworks - Langchain, Google Agent ..., Semantic Kernel,...
- Finetunning
- Temperature, top_t, top_k,... etc.
- System message
- MCP server
- function calling
📚 Documentation
See detailed guides and API reference in the docs or online.
🔒 Security
For information on reporting security vulnerabilities, see our Security Policy.
📦 Packages (for developers)
This library is divided into several packages, all are published from single monorepo. You can install all of them at once:
npm i ptbkOr you can install them separately:
⭐ Marked packages are worth to try first
- ⭐ ptbk - Bundle of all packages, when you want to install everything and you don't care about the size
- promptbook - Same as
ptbk - ⭐🧙♂️ @promptbook/wizard - Wizard to just run the books in node without any struggle
- @promptbook/core - Core of the library, it contains the main logic for promptbooks
- @promptbook/node - Core of the library for Node.js environment
- @promptbook/browser - Core of the library for browser environment
- ⭐ @promptbook/utils - Utility functions used in the library but also useful for individual use in preprocessing and postprocessing LLM inputs and outputs
- @promptbook/markdown-utils - Utility functions used for processing markdown
- (Not finished) @promptbook/wizard - Wizard for creating+running promptbooks in single line
- @promptbook/javascript - Execution tools for javascript inside promptbooks
- @promptbook/openai - Execution tools for OpenAI API, wrapper around OpenAI SDK
- @promptbook/anthropic-claude - Execution tools for Anthropic Claude API, wrapper around Anthropic Claude SDK
- @promptbook/vercel - Adapter for Vercel functionalities
- @promptbook/google - Integration with Google's Gemini API
- @promptbook/deepseek - Integration with DeepSeek API
- @promptbook/ollama - Integration with Ollama API
@promptbook/azure-openai - Execution tools for Azure OpenAI API
@promptbook/fake-llm - Mocked execution tools for testing the library and saving the tokens
- @promptbook/remote-client - Remote client for remote execution of promptbooks
- @promptbook/remote-server - Remote server for remote execution of promptbooks
- @promptbook/pdf - Read knowledge from
.pdfdocuments - @promptbook/documents - Integration of Markitdown by Microsoft
- @promptbook/documents - Read knowledge from documents like
.docx,.odt,… - @promptbook/legacy-documents - Read knowledge from legacy documents like
.doc,.rtf,… - @promptbook/website-crawler - Crawl knowledge from the web
- @promptbook/editable - Editable book as native javascript object with imperative object API
- @promptbook/templates - Useful templates and examples of books which can be used as a starting point
- @promptbook/types - Just typescript types used in the library
- @promptbook/color - Color manipulation library
- ⭐ @promptbook/cli - Command line interface utilities for promptbooks
- 🐋 Docker image - Promptbook server
📚 Dictionary
The following glossary is used to clarify certain concepts:
General LLM / AI terms
- Prompt drift is a phenomenon where the AI model starts to generate outputs that are not aligned with the original prompt. This can happen due to the model's training data, the prompt's wording, or the model's architecture.
- Pipeline, workflow scenario or chain is a sequence of tasks that are executed in a specific order. In the context of AI, a pipeline can refer to a sequence of AI models that are used to process data.
- Fine-tuning is a process where a pre-trained AI model is further trained on a specific dataset to improve its performance on a specific task.
- Zero-shot learning is a machine learning paradigm where a model is trained to perform a task without any labeled examples. Instead, the model is provided with a description of the task and is expected to generate the correct output.
- Few-shot learning is a machine learning paradigm where a model is trained to perform a task with only a few labeled examples. This is in contrast to traditional machine learning, where models are trained on large datasets.
- Meta-learning is a machine learning paradigm where a model is trained on a variety of tasks and is able to learn new tasks with minimal additional training. This is achieved by learning a set of meta-parameters that can be quickly adapted to new tasks.
- Retrieval-augmented generation is a machine learning paradigm where a model generates text by retrieving relevant information from a large database of text. This approach combines the benefits of generative models and retrieval models.
- Longtail refers to non-common or rare events, items, or entities that are not well-represented in the training data of machine learning models. Longtail items are often challenging for models to predict accurately.
Note: This section is not a complete dictionary, more list of general AI / LLM terms that has connection with Promptbook
💯 Core concepts
- 📚 Collection of pipelines
- 📯 Pipeline
- 🙇♂️ Tasks and pipeline sections
- 🤼 Personas
- ⭕ Parameters
- 🚀 Pipeline execution
- 🧪 Expectations - Define what outputs should look like and how they're validated
- ✂️ Postprocessing - How outputs are refined after generation
- 🔣 Words not tokens - The human-friendly way to think about text generation
- ☯ Separation of concerns - How Book language organizes different aspects of AI workflows
Advanced concepts
| Data & Knowledge Management | Pipeline Control |
|---|---|
|
|
| Language & Output Control | Advanced Generation |
|
|
🚂 Promptbook Engine
➕➖ When to use Promptbook?
➕ When to use
- When you are writing app that generates complex things via LLM - like websites, articles, presentations, code, stories, songs,...
- When you want to separate code from text prompts
- When you want to describe complex prompt pipelines and don't want to do it in the code
- When you want to orchestrate multiple prompts together
- When you want to reuse parts of prompts in multiple places
- When you want to version your prompts and test multiple versions
- When you want to log the execution of prompts and backtrace the issues
➖ When not to use
- When you have already implemented single simple prompt and it works fine for your job
- When OpenAI Assistant (GPTs) is enough for you
- When you need streaming (this may be implemented in the future, see discussion).
- When you need to use something other than JavaScript or TypeScript (other languages are on the way, see the discussion)
- When your main focus is on something other than text - like images, audio, video, spreadsheets (other media types may be added in the future, see discussion)
- When you need to use recursion (see the discussion)
🐜 Known issues
🧼 Intentionally not implemented features
❔ FAQ
If you have a question start a discussion, open an issue or write me an email.
- ❔ Why not just use the OpenAI SDK / Anthropic Claude SDK / ...?
- ❔ How is it different from the OpenAI`s GPTs?
- ❔ How is it different from the Langchain?
- ❔ How is it different from the DSPy?
- ❔ How is it different from anything?
- ❔ Is Promptbook using RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation)?
- ❔ Is Promptbook using function calling?
📅 Changelog
See CHANGELOG.md
📜 License
This project is licensed under BUSL 1.1.
🤝 Contributing
We welcome contributions! See CONTRIBUTING.md for guidelines.
You can also ⭐ star the project, follow us on GitHub or various other social networks.We are open to pull requests, feedback, and suggestions.
🆘 Support & Community
Need help with Book language? We're here for you!
- 💬 Join our Discord community for real-time support
- 📝 Browse our GitHub discussions for FAQs and community knowledge
- 🐛 Report issues for bugs or feature requests
- 📚 Visit ptbk.io for more resources and documentation
- 📧 Contact us directly through the channels listed in our signpost
We welcome contributions and feedback to make Book language better for everyone!
