npm i chalky / yarn add chalky
chalky
Table of Contents
About
Like chalk with fewer features, smaller in size (772 bytes), and self-contained (zero dependencies). Think of chalky like a 'stripped down', basic version of chalk..
chalky aims to provide a chalk-like experience, but for the most basic of console color features. Simple and small. 'Cheaply' add color to your console without worrying about the size of node_modules.
We're not quite hardened chalk, but we're still chalky :smirk:
Demos
Chaining
- Like chalk, chain methods together to change the foreground color, background color, add formatting (italic, bold, underline, etc..), for unique color/formatting combinations.
const chalky = require('chalky');
console.log(
chalky.italic.bgBlack.red.bold("Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet")
);- Output:

Color priority in chain
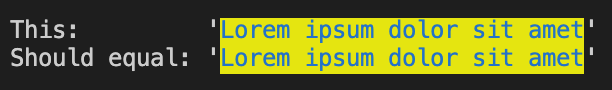
- The last color in the chain is what gets used:
const chalky = require('chalky');
// This line..
const a = chalky.red.green.blue.bgRed.bgBlack.bgYellow("Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet");
// ...is equivalent to this line
const b = chalky.blue.bgYellow("Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet");
console.log(`This: ${a}`);
console.log(`Should equal: ${b}`);- Output:
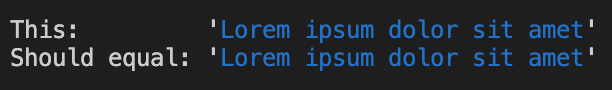
const chalky = require('chalky');
// This line..
const a = chalky.red.blue("Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet");
// ...is equivalent to this line
const b = chalky.blue("Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet");
console.log(`This: ${a}`);
console.log(`Should equal: ${b}`);- Output:
Rainbow
- Use
chalky.rainbow('Some string')to 'rainbowify' a string
const chalky = require('chalky');
console.log(
chalky.rainbow("Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet")
);- Output:

Properties
Foreground Colors:
blackredgreenyellowbluemagentacyanwhite
Background Colors:
bgBlackbgRedbgGreenbgYellowbgBluebgMagentabgCyanbgWhite
Formatting:
boldlightitalicunderlineblinkinversehidden
Why?
Two reasons...
I wanted to understand:
- How chalk was able to use properties with the same name as both a getter and method on the same object
- For example, you can do
chalk.blue('foo');andchalk.blue.bold('foo');(.blueis being used as both a method and getter)
- For example, you can do
How chalk was able to chain these properties/methods/getters
While modified, some of the code in this repo may resemble chalk as I followed the same logic.